The traditional means of scaling allow us to use the object origin as the center point to scale our objects in both directions on a single axis. There is, however, another way in which we can scale objects in Blender by using the object’s bounding box instead.
The scale cage tool is located on the tool shelf by clicking and hold of the scale tool icon to bring up the secondary menu. Select the scale cage option to switch to this form of scaling. The scale cage allows the user to scale in a single direction using anchor points positioned around the object’s bounding box.
This tool will be ideal when you don’t want to scale out your objects in multiple directions on a single axis, such as when trying to scale a building on top of a ground plane.
How To Activate The Scale Cage Tool?
The scale cage tool is initially hidden as it can only be accessed from the tool shelf. However, it is not immediately accessible from the tool shelf.
We have access to the various transforms, including the move, rotation, and scale tools. However, the scale tool is different from the scale cage tool. It’s not the one we’re looking for.
However, it is here where we will find the scale cage. If you take a closer look at the icon for the scale tool, you will notice in the bottom corner that we have a small arrow.
This indicates that there is a secondary menu associated with this button. Left-click and hold the left mouse button to bring up that secondary menu.
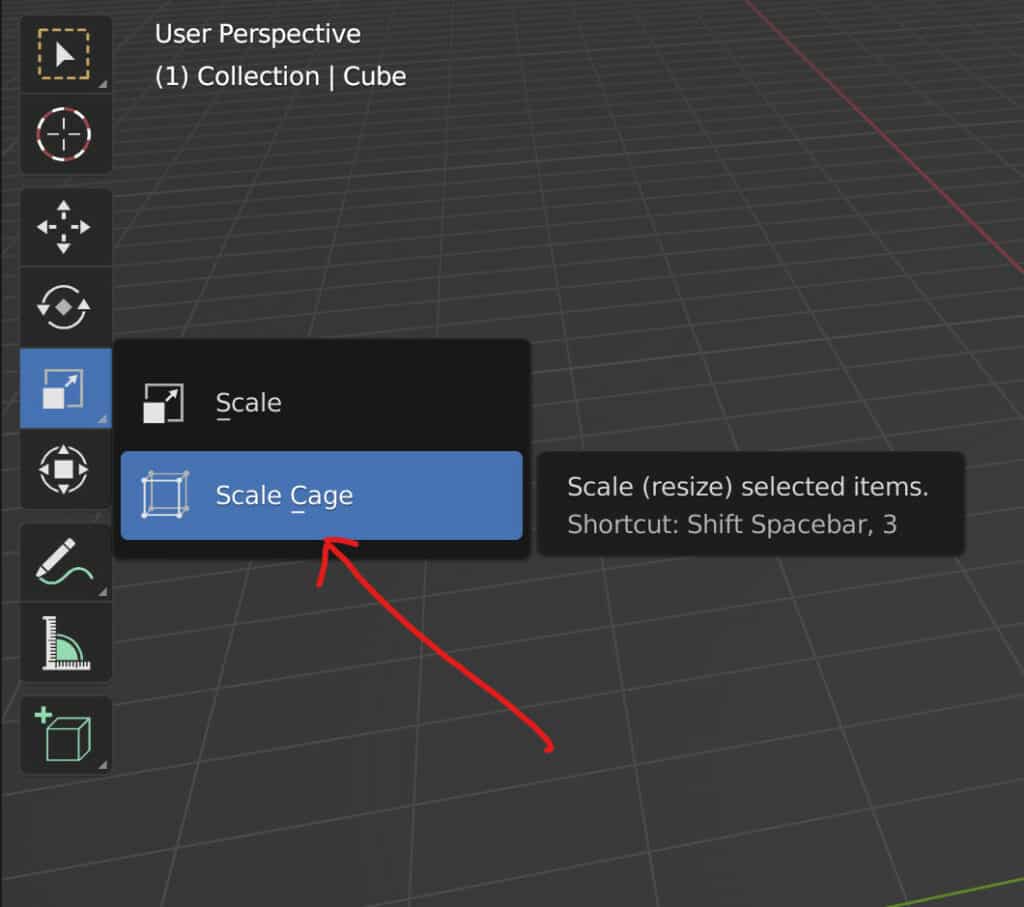
There should be two options here. The first is going to be for the traditional scale tool. The second is going to be for the scale cage tool. Select the scale cage, and then you will see the change occur in both the tool shelf and the 3D viewport.
How Does The Scale Tool Work?
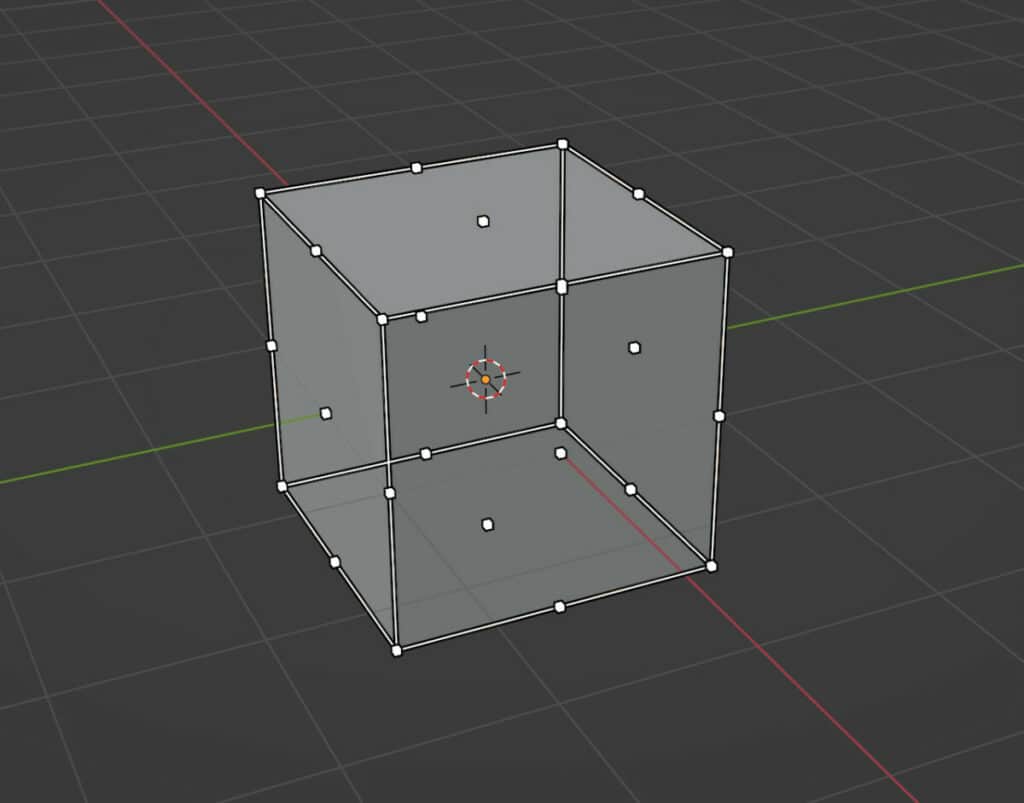
If we take a look at our objects, we will notice that there are a series of points dotted around our model.
These points are not connected to the model itself. Instead, they are connected to the bounding box generated by the models’ size.
If we were to change our cube object to something slightly more complicated, such as Suzanne, you would see what we mean.
A box is formed that surrounds the object; this box’s dimensions are the same as the object’s dimensions.
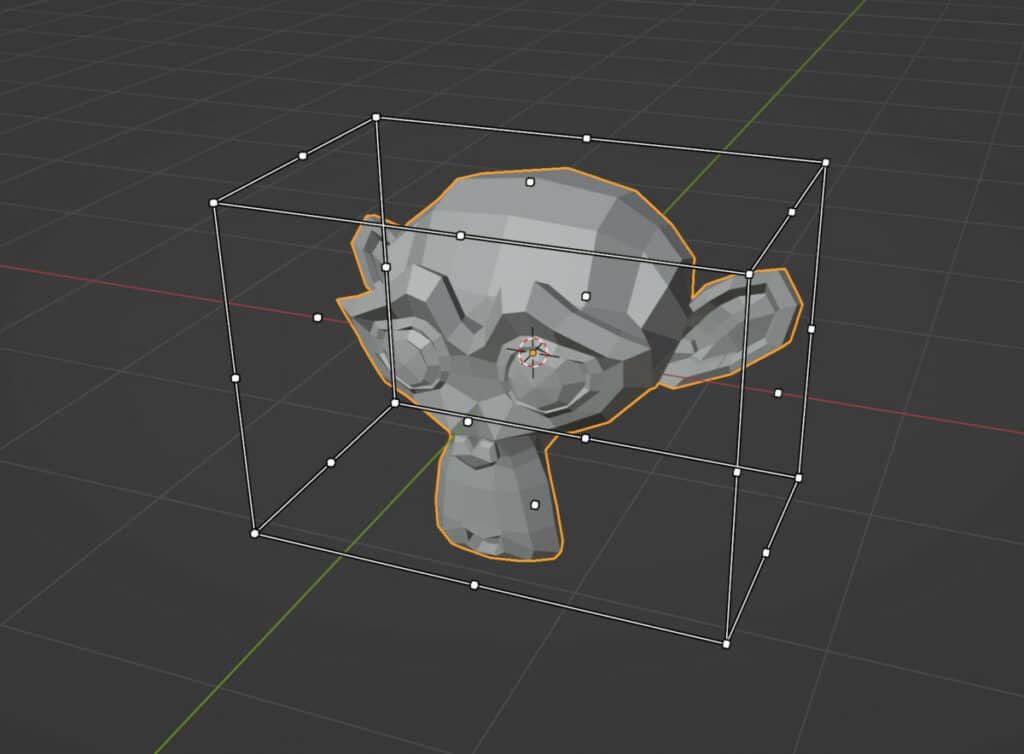
The various white dots we see around our box are the anchor points, and they are all paired with opposite points.
Starting with the points located in the center of each face, these points allow us to scale in a single direction on a single axis.
For example, if we were to click and drag on the middle white dots on the top face of our bounding box, we would be able to scale up on the Z axis.
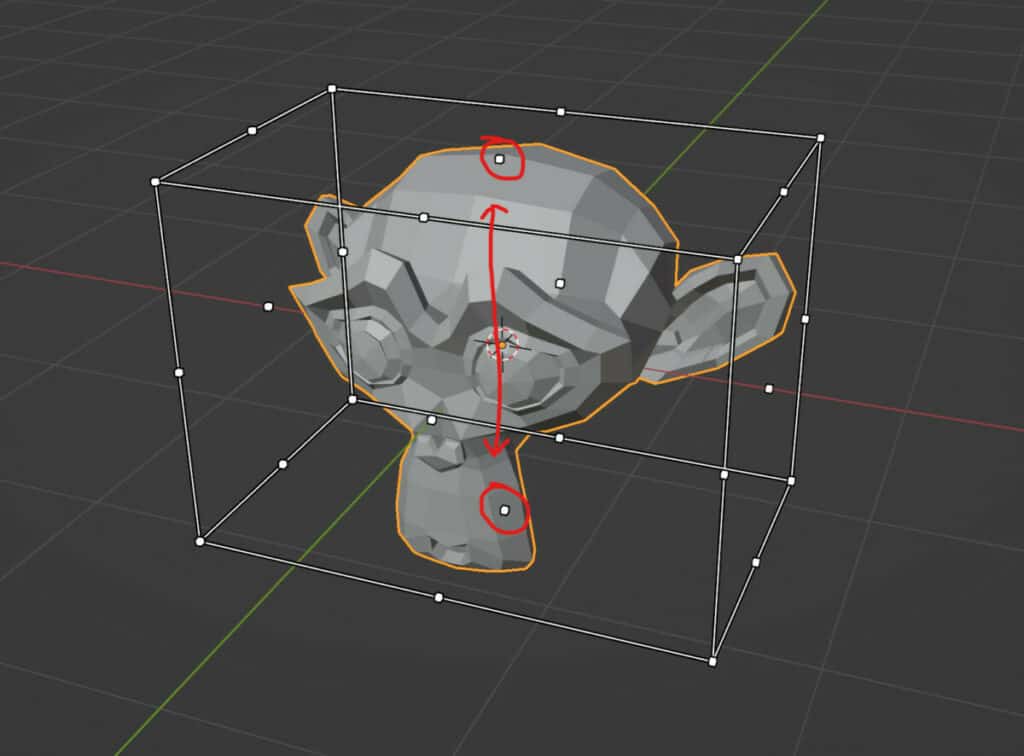
It does not scale from the anchor point that we select. Instead, it will scale from the dot at the bottom of the bounding box, which acts as the anchor point for this scaling method.
As previously mentioned, each white dot you will find with the scale cage tool has a paired dot that acts as the anchor point. So when you click and drag from any of these dots, its partner will act as the anchor for the scaling.
If you want to scale on two axes simultaneously, you can do so by clicking and dragging from any of the white dots on the edges of the box.
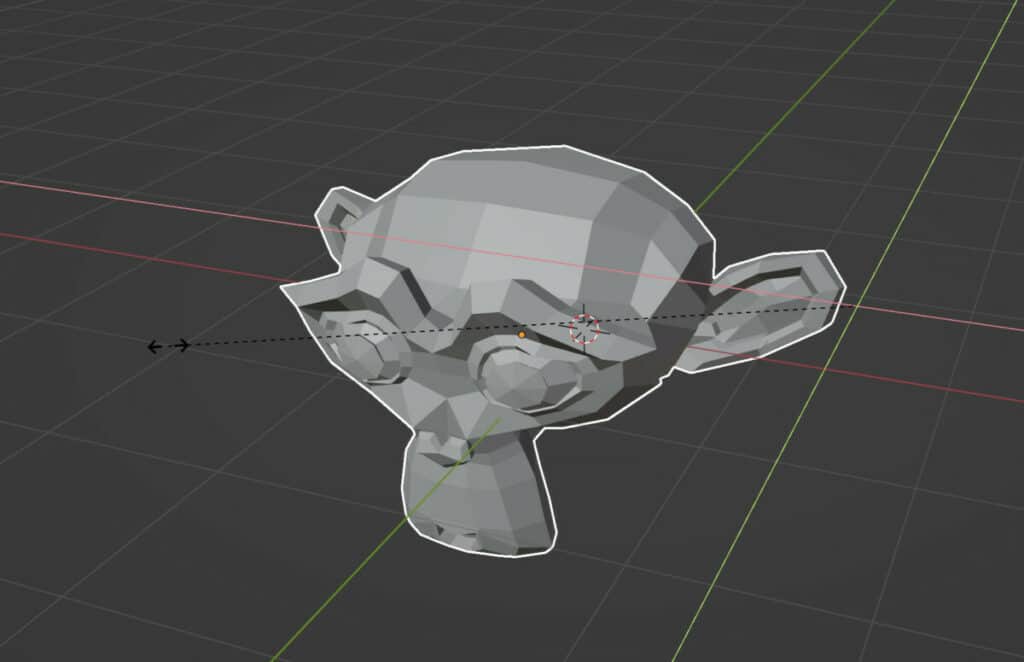
For example, clicking on an edge can allow you to scale out from the Y plane. Meanwhile, selecting a different edge would allow you to scale from the X plane. Different edges will allow you to scale your objects on different planes, so a little bit of practice may be required to understand which edge is associated with which plane.
Finally, we have the white dots on the corners of our bounding box, allowing us to scale in all three directions, X, Y, and Z.
However, anchor points are still used even with the vertices. They are still paired with other white dots to act as their anchors. So we can click and drag to scale out on all three axes, but one part of our model will always remain in place.
What Is The Difference Between The Scale Tool And The Scale Cage?
The critical difference between the scale tool and the scale cage tool is what is used as the point of reference. When it comes to the scale tool, the point of reference is always going to be the origin of the object.
When we use the traditional scale tool, and the origin is at the center of our model, then we’re going to scale up in both the positive and negative directions if our object origin is located at the center of our object.
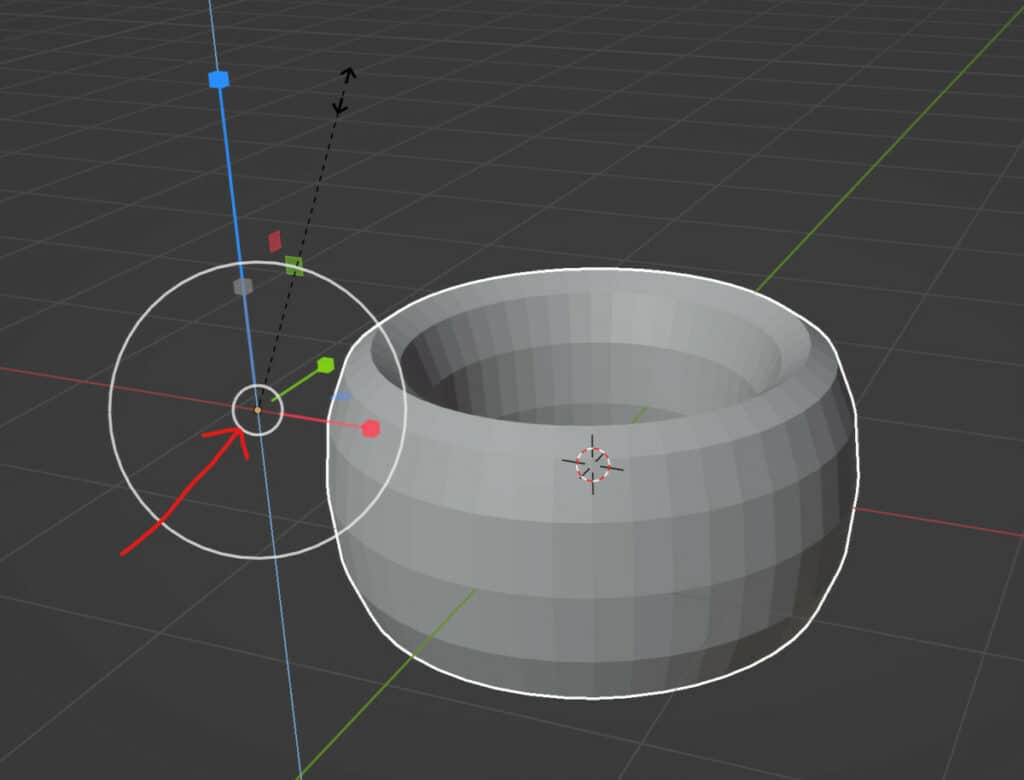
We can see this most clearly by using a simple object, such as a Torus, with the object’s origin at the center. If scaling on the Z axis, we would end up pushing the top side of the cube upwards, while the bottom side would be pushed downwards by the same amount.
To change this behavior so that we could only scale upwards on the Z axis, we would need to move the object origin solely positioned on the bottom face of the object.
This way, because of the origins of the object positioning, the cube would not sink below the origin of the object and would, therefore, only rise as it would be scaled.
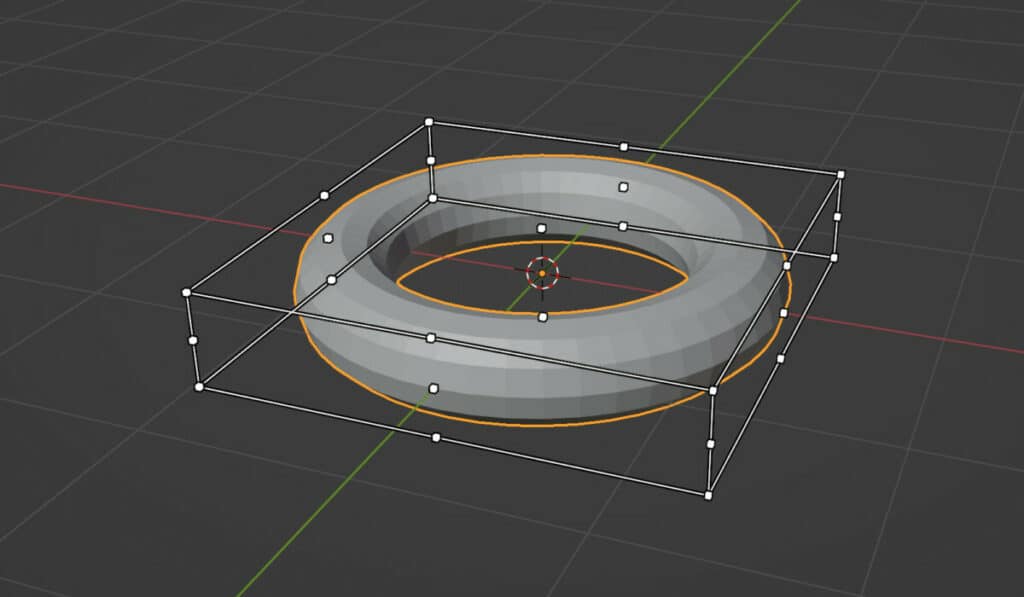
By contrast, the scale cage tool uses the bounding box of the objects to define the scaling. It does not use the object’s origin or its positioning at all.
Instead, it defines the bounding box, then uses the anchor points dotted around the bounding box as the point of reference for the scaling.
This method prevents us from ever scaling in both the positive and negative directions on a specific axis. It will always be one or the other with the scale cage tool.
Thanks For Reading
We appreciate you taking the time to read through the article. We hope you found the information you were looking for. If you are interested in learning more about the Blender software, you can check out a few of the articles we have listed below.
- How To Move Objects In The Viewport
- How To Rotate Objects In The Viewport
- How To Scale Objects In The Viewport
- Applying Your Object Transforms
- Clearing Your Object Transforms